Library Search FAQs
There are many ways to search for materials, starting from Catalog > Library Search. Following are some tips to use when performing a Basic or Power search.
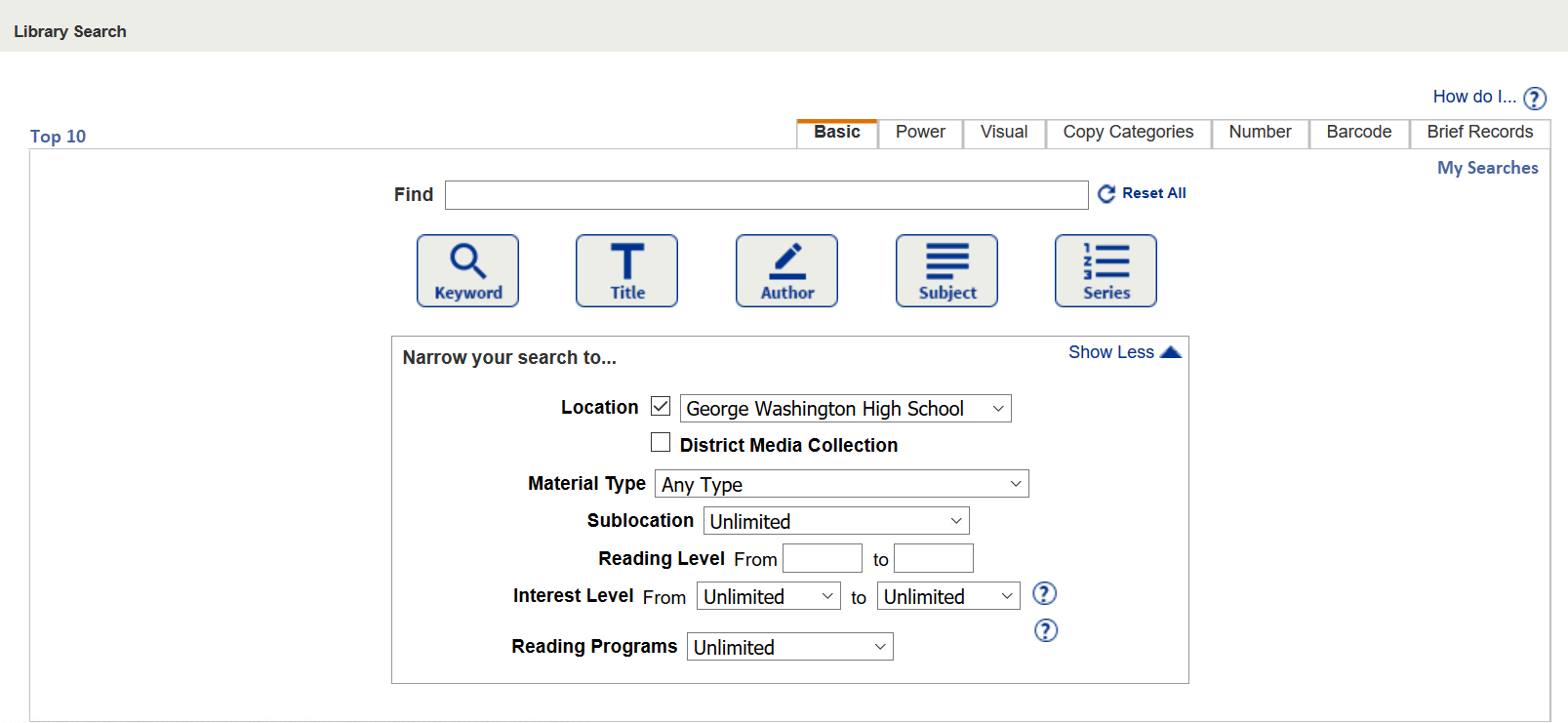
Search Terms
To start searching, you must enter either a complete word or a phrase (in quotes), and click a search button.
Searches are not case sensitive. For example, searches for give yourself goosebumps, Give Yourself Goosebumps and GIVE YOURSELF GOOSEBUMPS all return the same results.
When you enter a word or term and click Keyword, Destiny returns a list of items with that word almost anywhere in the record.
The Keyword search is best used when you have a complex search term that contains keywords from more than one of the other searches (author, title, subject or series).
For example, searching for Willy Wonka AND Dahl (Title and Author keywords) gets this result:
Charlie and the Great Glass Elevator by Roald Dahl.
Searching for Goosebumps AND Stine AND legend (Series and Author and Title keywords) results in just Legend of the Lost Legend by R. L. Stine. Had you just searched on just one of those three words, your results list may have been quite long. (There are about 100 books in the Goosebumps series, several authors named Stine, and dozens of books with legend in the title.)
Destiny ignores the punctuation in a search term.
If your search term includes words separated by a punctuation mark, such as a dash, double-dash, hyphen or slash, leave it out. When you leave it out, do not replace the punctuation mark with a space.
For example, if you are trying to find Camp Ghost-Away, enter camp ghostaway.
If you are trying to find Katie.com, enter katiecom.
If you do not know a complete word, or are not sure how to spell it, add an asterisk (*) to the end of what you do know. An asterisk can replace any number of letters at the end of a word. However, the * cannot be used as a word's first or second letter or have any letters after it.
|
Examples:
|
Use a question mark (?) to replace a single letter. You can use more than one question mark in a word, but it cannot be the first or last letter.
| Example: If you are not sure whether it is allegators, allagators or alligators, search for all?gators. A search for all* would also work, but the results list might be too long. |
You can also use a question mark to find multiple forms of a word. A search for wom?n finds both woman and women.
If you want to find a certain phrase, put quotation marks around it. For example, type "children's poetry" or "magic school bus".
Destiny ignores certain words, called stop words, in search terms. If you need to include stop words in your search term, switch to the Power tab, enter the term with the stop words, and select Starts with.
Depending on your library's preference, Destiny also may ignore leading articles such as A, An, Los, The and Un. You can leave them out of your search term.
If the title begins with an A that is not a leading article, such as A, my name is Ami or G is for Galaxy, put quotation marks around the title.
Destiny provides the following stop words. Your library may have a different list.
- a, an, and, are, as, at
- be, but, by
- for
- if, in, into, is, it
- no, not
- of, on, or
- such
- that, the, their, then, there, these, they, this, to
- was, will, with
To learn more, see Power Search.
You can create a search phrase from several distinct words or terms with Boolean operators between them. These operators – AND, OR, NOT – define the relationship between the words or phrases in your search term.
| Note: In a Basic search, you can type Boolean operators in the Find field; in a Power search, you can select them. |
Make sure to type the operators using uppercase letters:
- cats AND dogs gives you only the titles that mention both cats and dogs
- cats OR dogs gives you all the titles that mention cats or dogs
- cats NOT dogs gives you only the titles about cats that do not mention dogs
Keep in mind that AND narrows a search, giving you fewer results; OR expands a search, giving you more results.
Make sure, also, that you do not use OR if you mean NOT.
| example: You want to find a nonfiction book by Isaac Asimov that is not about science. If you search for asimov NOT fiction OR science, your results will not include fiction but will contain science. You should search for asimov NOT fiction NOT science. |
To learn more, see AND, OR, NOT.
If you misspell a search word, or Destiny cannot find your word, Destiny asks, Did you mean...?. If Destiny's word is correct, click the word to see the search results. If not, click Refine your search and try again.
| example: If you type elephnt, Destiny asks, Did you mean "elephant"?. Click elephant if that is the word you meant to enter. |
non-Follett and Follett
- Using a Basic or Power search, enter your search term.
- In the
Narrow your search to…
section, select one of the following from the Material Type drop-down: electronic Book (eBook) or Sound Recording (nonmusical).
- Click the applicable search button.
- Browse search results to select a resource.
On the Search Results page:
- Search results contain only publisher-hosted content owned by your school, even when you search across the district.
- Every eBook with a URL in an 856 tag displays an Open button.
- For non-Follett eBooks with more than one 856 tag, the Open button links to the first 856 tag in the record.
- For eBooks, click Open. For Audiobooks, click Play.
Search Results
There are tabs for different types of materials:
- Titles lists the media center materials matching your search term, including eBooks and audiobooks.
- Web Sites lists the websites that have information about the search term. If your media center subscribes to WebPath Express, each entry has a link to open the website.
- One Search lists the resources in your online databases, if your media center subscribes to One Search.
- Digital Resources lists videos, pictures and sound files from a digital provider, if your media center has them. Each entry has a link to play the resource.
You can add any of these materials and resources to a Resource List.
If your Search Results list is too large, refine your search, using a more exact term.
- If you use more words, you get fewer results. Use North American birds rather than just birds.
- Be as specific as you can be. Use marine biology rather than science.
- Put NOT (in uppercase letters) in front of each word that you do not want. For example, pets NOT cats NOT birds will give you titles about pets – all kinds of pets except for cats and birds.
If the Search Results list is still too long, or does not contain what you want, try a Power search.
To learn more, see Conduct a Power Search.
If you get too few results, you can either refine your search or browse through a list of library materials.
To refine your search:
- Use a more general term. For example, use history or war rather than Spanish-American war.
- Try adding similar words with OR (in uppercase letters) in front of each. For example, cars OR autos OR automobiles.
- Try using a similar or related word. For example, if biosphere produces no results, try entering atmosphere, or biology, or even life.
You could browse through a list: Just click Browse Subjects. Depending on the button you clicked, it might be Browse Titles, Browse Authors, Browse Series or Browse Subjects. You will not have a Browse... link if your search included limiters.
- To scroll through the list, click the arrows.
- To open a list of library materials, click an entry with a number in brackets.
- To open a list of websites, click an entry with a WebPath Express icon.
To erase your search term and any limiters you have set, click Reset All next to the Find field.
These are cross-references. If your library has them, you may see them when browsing. Your library uses them to point you to the correct term or to more information.
See means that the search term you used is listed under a different name.
For example, if you search for cars, the browse list may show cars See: automobiles. You can click that link to see the listing for automobiles. Next time, just search for automobiles.
See also means that, while your search term is correct, there are other topics containing related or additional information that may be useful to you.
For example, if you search for automobiles, your results could include automobiles See also: Ford automobiles. You can click that link to see books about those.
You can look up and repeat any previous searches you performed by clicking My Searches at the top of a search page.
On the Search History page that appears, you can redo any search by clicking its name.
You will not see My Searches until you perform at least one search.
To learn more, see Use Search History.
Use a Resource List to create and print a customized list of your search results. This can be useful when doing research and for finding the books on shelves.
- To add all of the items in the Search Results list to your list, click
Add Page to List at the top of the page.
- To add just the ones you are interested in, click Add to this List next to each one. Then, to see, edit and print your List, click Resource Lists on the side menu.
If you do not want to make a custom list, you can print the entire Search Results list by clicking Printable and then using your browser's Print option.
To learn more, see Resource Lists.
For more information on training resources, visit Follett Community.